Big Data Characteristics : (Volume, Velocity, Variety ,Veracity,Validity and value...)
For a dataset to be considered Big Data,
it must possess one or more characteristics that require accommodation in the
solution design and architecture of the analytic environment.
This explores the five Big Data
characteristics that can be used to help differentiate data categorized as
“Big” from other forms of data.
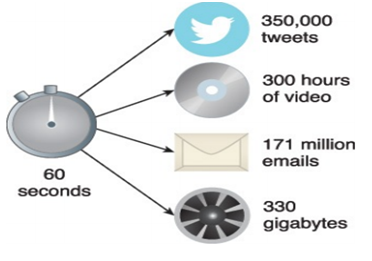
1. Volume – Scale of Data
• online transactions, such as point-of-sale and banking
• scientific and research experiments.
• sensors, such as Global Positioning System(GPS), RFIDs, smart meters and telematics.
• social media, such as Facebook and Twitter.
Velocity refers to the high speed of accumulation of data. In Big Data velocity data flows in from sources like machines, networks, social media, mobile phones etc.
There is a massive and continuous flow of data. This determines the potential of data that how fast the data is generated and processed to meet the demands.Sampling data can help in dealing with the issue like ‘velocity’.
Example: There are more than 3.5 billion searches per day are made on Google. Also, Facebook users are increasing by 22%(Approx.) year by year.
It refers to nature of data that is structured, semi-structured and unstructured data.It also refers to heterogeneous sources.Variety is basically the arrival of data from new sources that are both inside and outside of an enterprise. It can be structured, semi-structured and unstructured.
Structured data: This data is basically an organized data. It generally refers to data that has defined the length and format of data.
Semi- Structured data: This data is basically a semi-organized data. It is generally a form of data that do not conform to the formal structure of data. Log files are the examples of this type of data.
Unstructured data: This data basically refers to unorganized data. It generally refers to data that doesn’t fit neatly into the traditional row and column structure of the relational database. Texts, pictures, videos etc. are the examples of unstructured data which can’t be stored in the form of rows and columns.
It refers to inconsistencies and uncertainty in data, that is data which is available can sometimes get messy and quality and accuracy are difficult to control.










No comments:
Post a Comment